Vitex agnus-castus L.
In front of our house in Chania is an old building place, where you can see the structural skeleton of a new to build house. There is a rumor that a father intended to build a house for the bridal dowry, the "proika", for his daughter. For some unknown reason, he never finished the house. And such desolated places are the perfect place to look for Vitex agnus-castus. Another place where you can find many of these shrubs, is at the northern shores of the only sweet water lake in Crete, the lake of Kournas (Limni Kournas).
Vitex agnus-castus is not only botanically interesting: it plays a role in Greek mythology and has been used in medicine for many centuries. Pliny the Elder, the Greek natural historian (AD 23–79) advised to use the plant to promote menstruation, to purge the uterus and to promote the flow of milk in new mothers. Hippocrates (4th Century BC) and later Dioscorides (in his De Materia Medica, written in AD 77) also say that it was used for diseases of the uterus. According to Dioscorides a bunch of branches of the tree give protection against attacks of wolves.
In the Greek mythology the Chastetree was associated with chastity and virginity. According to Dioscorides (1st century AD) and Theofrastus (3d century AD) the tree was called agnos, from the Greek word for holy, pure, chaste.
In the antique Greek world, people believed that the plant calmed sexual passion and the Chaste tree, as its name implies, has been used as an anaphrodisiac, because .......
Vitex agnus-castus is not only botanically interesting: it plays a role in Greek mythology and has been used in medicine for many centuries. Pliny the Elder, the Greek natural historian (AD 23–79) advised to use the plant to promote menstruation, to purge the uterus and to promote the flow of milk in new mothers. Hippocrates (4th Century BC) and later Dioscorides (in his De Materia Medica, written in AD 77) also say that it was used for diseases of the uterus. According to Dioscorides a bunch of branches of the tree give protection against attacks of wolves.
In the Greek mythology the Chastetree was associated with chastity and virginity. According to Dioscorides (1st century AD) and Theofrastus (3d century AD) the tree was called agnos, from the Greek word for holy, pure, chaste.
In the antique Greek world, people believed that the plant calmed sexual passion and the Chaste tree, as its name implies, has been used as an anaphrodisiac, because .......
because it was believed that the flowers and fruits decreased the sex drive. Throughout the Middle Ages medical writers in Europe simply recopied the ancient Greek and Roman sources, and Chasteberry fruits that look like pepper and smell and taste like pepper, were used as a pepper substitute to suppress the "lusts of the flesh", and to treat female disorders. Its common name Monkspepper refers to the use of the monks in the Middle Ages to chew on the dried berries in order to be better able to fulfill their promises of celibacy. Scientific research however has found no bases for this popular belief.
The names that were used for the Chastetree give an indication of its historical reputation. The early Christians probably confused the ancient Greek name ágnos with the similar Greek term agnós and with the Latin agnus (lamb, the symbol of purity). Castus comes from the Latin castitas, meaning chastity.
The genus name Vitex means "to bend, to fold", because the flexible branches of the tree were used in the construction of plaited fences. The modern Greek name for the tree is lygariá and is probably also derived from the old Greek word for bending, folding. Even nowadays the young stems are being used in basket making, and from the leaves, seeds, and the roots, a yellow dye is obtained.
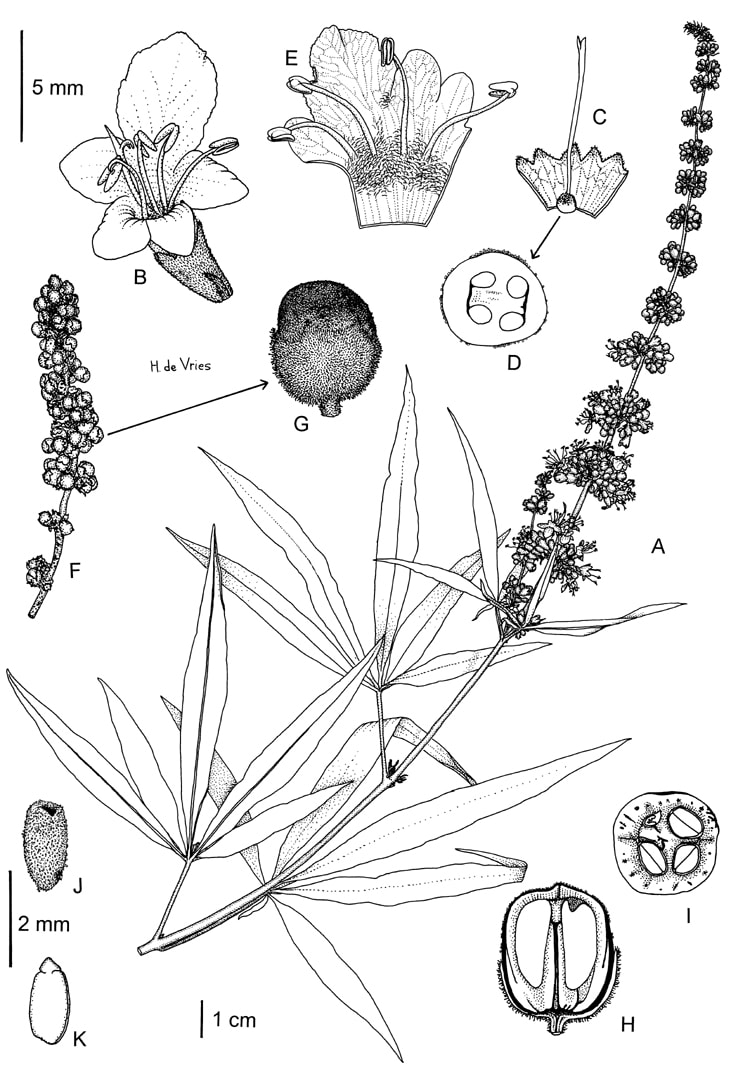
The Chaste Tree or Monkspepper is a large deciduous shrub, up to 3 m (according to Flora Europaea up to 6 m, but I never found a bush that high). The young twigs are four-angled, older twigs tend to be more rounded. The leaves are petiolate and composed of 5 to 7 stipitate leaflets; the longest leaflets in the middle are about 10 cm, lance shaped, palmately arranged and acuminate, on long leaf stems. The border of the leaflet is entire. The underside of the leaflets is whitish from the white hairs, the upperside is glabrous and dark green. The leaves are oppositely arranged along the ridged upper stems.
The flower spikes form mainly near or at branch ends and are of a variety of colors: lavender, blue, pink and white are the typical colors, and are weakly aromatic. The calyx is small, with 5 lobes, see detail C. The Chasteberry is a member of the Lamiaceae (formerly Verbenaceae) family, so the flowers are 4- to 5-merous and zygomorphic : the 8 - 10 mm corolla is 2-lipped, the upper lip with 2 and the lower with 3 lobes. The calyx and the corolla are covered with whitish hairs. The upper half of the superior ovary is covered with black tiny spheres. This ovary is initially 1-locular, but soon (before flowering) becoming 2- to 4-locular by the development of septa; there is one ovule in each loculus. The long style is terminal. In the Lamiaceae (Verbenaceae) there are often 2 long and 2 short stamens and/or they are inserted at different heights, but in the Chaste tree this is not very clear. The corolla tube is closed by a ring of hairs, see E.
The fruit is a drupe, grey to black, nearly twice as long as the remaining calyx, see details G, H. The bitter and astringent taste is caused by flavonoids and iridoid glycosides . Seldom all 4 ovules develop into seeds, see detail I.
Distribution: it is originally a plant of the Mediterranean region of southern Europe, northern Africa, and western Asia, but now it is found throughout warmer parts of the United States, Africa and Asia.
Large surveys were done in Germany to study the effect of Vitex on women diagnosed as suffering from PMS. The Vitex fluid extract used was Agnolyt. The treatment was assessed by both patient and practitioner It was noted that in 90% of cases symptoms were completely relieved and symptoms such as headaches, sore breasts, bloating and fatigue and psychological changes such as increased appetite, sweet cravings, nervousness or restlessness, anxiety, depression, mood swings and lack of concentration were all reduced..
A controlled clinical trial in England found a significant improvement in the treatment of PMS. It seems that the use of Vitex agnus-castus has a positive influence on a healthy menstruation and other applications connected with the female metabolism. It must be noted however that no individual constituent of Vitex has been shown to have an intrinsic hormonal activity, and the chemical composition responsible for its action has not yet been isolated.
The names that were used for the Chastetree give an indication of its historical reputation. The early Christians probably confused the ancient Greek name ágnos with the similar Greek term agnós and with the Latin agnus (lamb, the symbol of purity). Castus comes from the Latin castitas, meaning chastity.
The genus name Vitex means "to bend, to fold", because the flexible branches of the tree were used in the construction of plaited fences. The modern Greek name for the tree is lygariá and is probably also derived from the old Greek word for bending, folding. Even nowadays the young stems are being used in basket making, and from the leaves, seeds, and the roots, a yellow dye is obtained.
The Chaste Tree or Monkspepper is a large deciduous shrub, up to 3 m (according to Flora Europaea up to 6 m, but I never found a bush that high). The young twigs are four-angled, older twigs tend to be more rounded. The leaves are petiolate and composed of 5 to 7 stipitate leaflets; the longest leaflets in the middle are about 10 cm, lance shaped, palmately arranged and acuminate, on long leaf stems. The border of the leaflet is entire. The underside of the leaflets is whitish from the white hairs, the upperside is glabrous and dark green. The leaves are oppositely arranged along the ridged upper stems.
The flower spikes form mainly near or at branch ends and are of a variety of colors: lavender, blue, pink and white are the typical colors, and are weakly aromatic. The calyx is small, with 5 lobes, see detail C. The Chasteberry is a member of the Lamiaceae (formerly Verbenaceae) family, so the flowers are 4- to 5-merous and zygomorphic : the 8 - 10 mm corolla is 2-lipped, the upper lip with 2 and the lower with 3 lobes. The calyx and the corolla are covered with whitish hairs. The upper half of the superior ovary is covered with black tiny spheres. This ovary is initially 1-locular, but soon (before flowering) becoming 2- to 4-locular by the development of septa; there is one ovule in each loculus. The long style is terminal. In the Lamiaceae (Verbenaceae) there are often 2 long and 2 short stamens and/or they are inserted at different heights, but in the Chaste tree this is not very clear. The corolla tube is closed by a ring of hairs, see E.
The fruit is a drupe, grey to black, nearly twice as long as the remaining calyx, see details G, H. The bitter and astringent taste is caused by flavonoids and iridoid glycosides . Seldom all 4 ovules develop into seeds, see detail I.
Distribution: it is originally a plant of the Mediterranean region of southern Europe, northern Africa, and western Asia, but now it is found throughout warmer parts of the United States, Africa and Asia.
Large surveys were done in Germany to study the effect of Vitex on women diagnosed as suffering from PMS. The Vitex fluid extract used was Agnolyt. The treatment was assessed by both patient and practitioner It was noted that in 90% of cases symptoms were completely relieved and symptoms such as headaches, sore breasts, bloating and fatigue and psychological changes such as increased appetite, sweet cravings, nervousness or restlessness, anxiety, depression, mood swings and lack of concentration were all reduced..
A controlled clinical trial in England found a significant improvement in the treatment of PMS. It seems that the use of Vitex agnus-castus has a positive influence on a healthy menstruation and other applications connected with the female metabolism. It must be noted however that no individual constituent of Vitex has been shown to have an intrinsic hormonal activity, and the chemical composition responsible for its action has not yet been isolated.